全新無鉛、符合 RoHS 標準的雙焊墊石英晶體,採用金屬密封技術

作者:時脈產品設計經理 Jack Chou
數位電子電路通常使用系統時鐘,依照嚴格的週期間隔執行工作任務。透過結合石英晶體 (或諧振器) 與主動式電子振盪器電路,可以打造實現這項功能的穩定系統時鐘。設計人員在設計以石英為基礎的振盪器電路時,需要詳細瞭解石英晶體的特性,才能使設計符合目標產品應用的要求。
本文介紹並說明一款全新石英晶體系列的設計規格,該系列產品由 Diodes 公司 (Diodes) 製造,符合 RoHS 標準,具有雙焊墊。相較於採用玻璃密封設計的同級石英晶體,Diodes的產品採用金屬密封技術,從而實現真正的無鉛化。
Diodes 的雙焊墊 FE/FEQ 和 FT/FTQ 系列
Diodes 研發出的雙焊墊設計封裝的石英晶體,類似於現有的雙焊墊玻璃密封封裝,不同之處在於採用金屬密封 (見圖 1)。因此,這類石英晶體的佔用空間與玻璃密封裝置相同,但不含鉛。
圖 1. 玻璃密封元件 (左) 和金屬密封元件 (右)
雙焊墊的 FE/FEQ 5x3.2mm 和 FT/FTQ 3.2x2.5mm 系列是金屬密封元件,包含一個了超微型 AT 切割石英晶體諧振器,並採用標準陶瓷封裝,可取代傳統的玻璃雙焊墊封裝。FEQ 和 FTQ 系列元件符合 AEC-Q200 Grade 0 等級 (150°C) 標準,通過 PPAP,由 IATF 16949 標準認證的生產設施製造,專為汽車產品應用所設計。
和玻璃密封比較,雙焊墊金屬密封元件的各項參數表現都類似或是更佳,如下表 1 所示:
|
關鍵參數 |
DIODES FE/FEQ 系列雙焊墊 |
玻璃雙焊墊 |
|
頻率範圍 (基本) |
8 ~ 50MHz |
類似 |
|
頻率範圍 3OT |
50 ~ 125MHz |
類似 |
|
頻率容差 (25°C) |
15ppm |
30ppm |
|
ESR |
40 ~ 80Ω |
類似 |
|
驅動功率 |
200µW |
類似 |
|
完全無鉛 |
是 |
否 |
表 1. 雙焊墊金屬密封元件效能比較
下圖說明兩種封裝類型的長期穩定性,元件的效能隨著時間增加而略微提升。
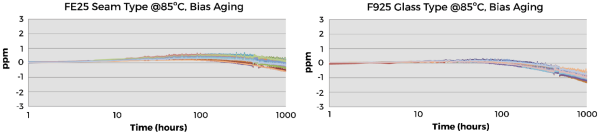
圖 2. 石英晶體在 85°C 下經過 1008 小時後的長期穩定性
石英晶體的技術原理
頻率
石英晶體的基頻以千赫茲 (kHz) 或兆赫 (MHz) 表示。頻率可精確到七位有效數字。
泛音(Overtones)
石英晶體最簡易的使用方式是在基頻下運作,但泛音模式下運作卻能發揮特有的優勢。泛音頻率是基頻的整倍數,這表示石英晶體的基頻可以遠低於預期的工作頻率,因此更容易製造且不易損壞。泛音石英晶體的主要應用於頻率高於 50MHz 的產品。在泛音模式下使用石英晶體時,電子電路設計必須確保石英晶體只在其泛音模式運作,而不會在基頻模式下運作。為實現這一點,射頻電路設計需包含一個調諧電路,確保振盪器中的回授發生在泛音頻率並抑制基頻。
切割
雖然石英晶體切割方式有無限多種,但其中幾個方式具有特定屬性及名稱,例如 AT、IT 和 SC。在振盪器工作頻率為 500kHz 至 300MHz 的電子元件中,使用最多的是 AT 切割石英晶體,因為這種切割在特定工作溫度下具有高 Q 值和頻率偏差對稱性。
校正容差 (FL)
也稱為頻率精度,以百萬分之一 (ppm) 為單位,通常指在 25°C 條件下。
負載電容 (CL)
此外部電容在電抗曲線上設置一個石英晶體的諧振點。此電容為實際應用中石英晶體的預期串聯電容。
等效串聯電阻 (ESR)
ESR 為串聯諧振石英晶體在額定驅動功率和調諧工作頻率下的等效歐姆電阻。
工作溫度範圍 (TR)
此溫度範圍以 °C 為單位,用於指定標示的頻率穩定性。多數石英晶體可在更寬的範圍內工作,但無法保證穩定在指定值內。這個較寬的範圍即為工作溫度範圍。存放溫度範圍是指存放石英晶體期間性能不會下降的溫度範圍,一旦回到工作溫度範圍,石英晶體將恢復正常工作。
頻率穩定性 (F/T)
此特性指定在整個工作溫度範圍內的頻率偏差,單位為 ppm。石英晶體坯的切割類型和角度會影響石英晶體如何隨溫度而變化。切割類型 (SL、DT、AT 等)主要取決於所需頻率,而指定的穩定性和工作溫度範圍則決定了切割的精確角度。
驅動功率 (DL)
驅動功率是石英晶體所消耗的功率,通常以微瓦 (μW) 或毫瓦 (mW) 為單位。可透過測量流過石英晶體的激發電流來計算驅動功率。
封裝密封
石英晶體通常以陶瓷為底座封裝,密封後能在較長的時間內 (通常為 15 年以上) 保持恆定的效能。石英晶體元件有兩種密封方式:金屬密封和玻璃密封。金屬密封使用電阻熱來焊接金屬蓋與陶瓷底座。玻璃密封則是靠熔化陶瓷頂端和底座之間的玻璃料(二氧化矽)來實現密封。
封裝焊墊
除了各種封裝尺寸外,石英晶體還可以分成四焊墊和雙焊墊封裝。雙焊墊元件具有卓越的焊接能力,可靠性更高,因此廣泛應用於汽車產品應用。目前所有雙焊墊石英晶體元件都使用玻璃密封法,因為製造成本通常較低。不過,這種密封法的問題在於玻璃料含有一定量的鉛 (Pb)。因此,使用這些含鉛石英晶體的終端產品可能需要申請 RoHS 豁免。
符合汽車規格 - 通過 AEC 認證,於支援 PPAP 文件的 IATF 16949 認證設施製造。
所有其他商標均為個別持有人的財產。
© 2024 Diodes Incorporated.版權所有。
